The advent of 5G technology has revolutionized the world of Internet of Things (IoT), enabling faster and more reliable connectivity for a wide range of devices. One crucial aspect of 5G IoT is the frequency bands used for communication. In this article, we will explore the 5G IoT frequency bands, their significance, and how they impact the deployment of IoT devices. This content is presented by https://www.arqweb.com/
Introduction to 5G IoT Frequency Bands
As 5G networks continue to roll out worldwide, the allocation of frequency bands for IoT devices has become a crucial consideration. Frequency bands refer to specific ranges of electromagnetic spectrum frequencies that are allocated for wireless communication. In the case of 5G IoT, these frequency bands are designated for the exchange of data between IoT devices and the network infrastructure. Find out how does 5g technology enhance the internet of things iot.
Sub-6 GHz Frequency Bands
The 5G IoT landscape includes several frequency bands, and the most widely deployed bands are those below 6 GHz, commonly referred to as sub-6 GHz bands. These bands offer a good balance between coverage area and data transfer speeds, making them suitable for various IoT applications.
1. Band n1 (2100 MHz)
The n1 band operates at a frequency of 2100 MHz and is primarily used for IoT applications that require reliable coverage and moderate data transfer rates. It offers improved indoor penetration compared to higher frequency bands, making it suitable for smart home devices, asset tracking, and industrial IoT applications.
2. Band n3 (3500 MHz)
The n3 band operates at a frequency of 3500 MHz and provides a higher data transfer rate compared to the n1 band. It is commonly used for IoT applications that require faster data transmission, such as high-definition video surveillance, connected vehicles, and smart city infrastructure.
3. Band n5 (850 MHz)
The n5 band operates at a frequency of 850 MHz and offers excellent coverage range and penetration capabilities. It is well-suited for IoT applications in rural areas, agriculture, and environmental monitoring, where wide coverage and long-range communication are essential.
Millimeter Wave (mmWave) Frequency Bands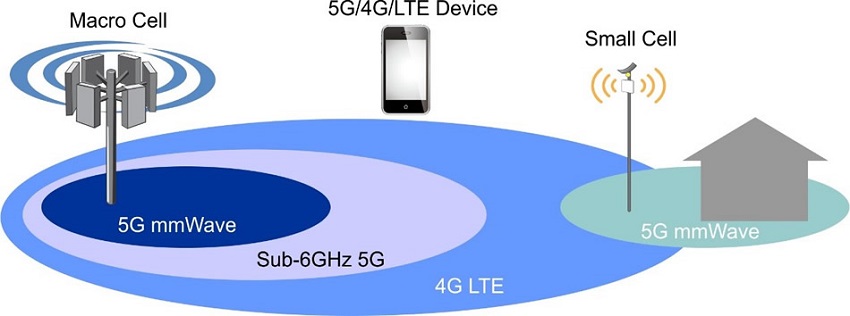
Apart from the sub-6 GHz bands, 5G IoT also utilizes millimeter wave (mmWave) frequency bands. These high-frequency bands offer incredibly fast data transfer speeds but have limited coverage areas. They are ideal for dense urban environments and specific use cases that demand ultra-low latency and high bandwidth.
4. Band n257 (28 GHz)
The n257 band operates at a frequency of 28 GHz and is commonly used for high-speed and low-latency IoT applications. It enables real-time data processing and is suitable for applications like autonomous vehicles, remote surgery, and virtual reality experiences.
5. Band n261 (39 GHz)
The n261 band operates at a frequency of 39 GHz and provides similar capabilities to the n257 band. It offers high bandwidth and low latency, making it suitable for IoT applications that require ultra-fast data transfer, such as industrial automation, augmented reality, and advanced robotics.
Conclusion
As the world embraces the era of 5G IoT, understanding the frequency bands allocated for IoT communication becomes crucial. The sub-6 GHz bands strike a balance between coverage and speed, catering to a wide range of IoT applications. On the other hand, the millimeter wave bands provide blazing-fast data transfer speeds but are limited to specific use cases.



